How to Increase Your Credit Score


When did you realize your credit score was critical to practically everything you did as an adult?
For me, it was when I learned how the credit card options for people with great credit were significantly better than for people who had average or below credit scores. If you have good to great credit, you get access to credit cards with huge sign-up bonuses and rewards.
If you don’t, your options are less attractive and you have to work towards improving your score before you can start applying for great credit cards.
But credit cards are just one small part — if you don’t have good credit, it can be difficult to get a rental apartment, a cell phone, and many other seemingly unrelated necessities.
So today, we’re going to talk about credit scores and how to improve yours.
To start, there is only one credit score that matters, and that’s the FICO Credit Score of Fair Isaac Corporation.
In this guide, I show you every step you can take to legitimately increase your credit score so you can, at the very least, be better than the average.
Your credit score is a number between 300 and 850, higher is better. It’s a measure of how likely you are to default (fail to pay) on a loan, the lower the number the greater the risk.
Your credit score is made up of five factors (image from FICO):
You can review your credit score for free with tools like Credit Sesame.
That’s it!
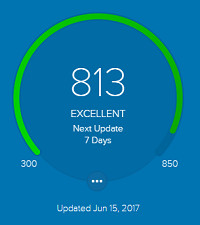
The key to increasing your credit score is to improve those five factors from the image above.
This guide is broken up into three sections:
It’s possible, especially early on, that you might not have a credit score at all or the dreaded “not enough credit history.” It’s hard to get a loan when you’ve never had a loan before. But there are a few things you can do to establish a credit history.
If used responsibly, these options will start reporting positive information to your credit report. This will establish some credit history and prove to future lenders that you do pay off your loans.
One note: Only become an authorized user on someone’s credit card if you know they pay their bills on time. If they pay late, that will go on your credit report as well. You can get that removed, but it’s a hassle that can be avoided if you pick someone trustworthy.
To learn more about establishing credit, review our guide to How to Establish Credit.
Be extra diligent and avoid the following at all costs.
They will reduce your credit score far more than any suggestions we make about improving it.
Enough doom and gloom, what can you do to increase your score?
Related: What Will Happen to Your Credit Score if You Do Not Manage Your Debt Wisely
From here, it’s straightforward – keep making those payments and keep an eye on your credit reports.
How do you make sure you never miss a payment?
Two steps:
How do I keep an eye on your credit reports?
The law states that you can get access to your credit reports every single year. I review each credit report on a rotating schedule, one every four months. Equifax in the Spring, Experian in the Summer, and Transunion in the Fall – all via AnnualCreditReport.com – the only place to go for your credit report.
Monitor “score” with free services
On a more regular basis I log into services at Credit Sesame, Credit Karma, and Quizzle that monitor my scores for free. They don’t provide FICO credit scores but they do offer the proprietary scores from the credit bureaus, which is good enough to act as a “canary in the coal mine” type of alert to changes.
For example, when I log into Credit Karma I see a VantageScore 3.0 from TransUnion and from Equifax.
If I see any big numerical moves, I know I need to review that credit report. A small dip, like 1 point on Equifax, isn’t worth investigating.
The following tools are available for those with poor or no credit. The key to getting a loan when you have poor credit is to reduce the risk to the lender as much as possible.
For example, secured credit cards require you to put down a deposit, then your credit limit is the amount of your deposit. This protects the lender because if you don’t pay back the loan, they can use your security deposit to recoup the funds. Since there is no risk of the lender losing money, they are willing to take a chance on you and give you the opportunity to build a positive credit history.
Experian Boost is not a loan, it is a free service offered by Experian that can increase your score by reporting on time payments you make to your bills. So if you pay things like rent, utilities, and insurance, your on-time payments can be reported to Experian.
This allows for a positive credit history without taking out a loan. You just pay your bills like normal.
Here’s our full Experian Boost review to learn more.
Secured credit cards work just like regular credit cards, except you have to put down a deposit. How much you put down will determine your credit limit. So if you submit a $500 deposit, you will have a $500 credit limit.
Once you receive the card, however, it works just like any other credit card. You make purchases, and each month, you will be required to make at least the minimum payment by the due date. Your payment history will be reported to the credit bureaus.
Some secured cards automatically upgrade to an unsecured card after a period of time, usually around six months — assuming responsible use.
Some of the newer fintech companies are offering what they’re calling “credit building cards.” These are credit cards that work similarly to secured cards, but you don’t have to put down a deposit. Instead, the cards are tied to your checking account, and when you spend money on the card, the money is instantly withdrawn from your checking account and set aside. The money that is set aside is then used to pay the card in full on the due date.
The on-time payment is then reported to the credit bureaus, and you build a positive credit history.
One example of this is the Chime Credit Builder Card.
Credit builder loans are a bit of a misnomer because they don’t really work like loans. Instead, it’s more of a forced savings plan that also builds credit.
With traditional loans, when you take out a loan, you instantly receive the proceeds and then repay the debt over time. A credit builder loan works in reverse. You make payments into a savings account with the lender, and when your loan is complete, you will receive the balance of the account.
Let’s look at a simplified example. Say you take a $1,000 credit builder loan with $100 payments for 10 months. Each month, you will pay $100, and after 10 months, you will have $1,000 in a savings account that will be released to you.
Note that in a real loan, there are fees involved, so you would not get the full $1,000. However, you would have 10 months of on-time payments reported to credit bureaus and a good amount of savings built up, so the cost may be worth it.
An example of this type of loan is the Self Credit Builder Loan.
If your score is low because of previously made mistakes with credit, credit repair can be a viable option to try to improve it. Whenever there are bad marks on your report, those marks stay on for a period of time and keep your score low. These are events like a late payment or bankruptcy.
What credit repair companies do is take some action to try to remove those black marks. They will do things like dispute negative items or take other steps to get them removed. They’re going to be expensive but if you have a need, they can be worth it if they are successful. They are only increasing your score by removing the negative items.
Alternatively, you can also use credit repair software (instead of companies) to help you with the process for a smaller cost. The benefit of credit repair software is that you are doing the work, so you know exactly what is happening. It takes more time, but it costs less, and you are in full control.
If you have no negative items (or no credit history at all), they cannot help you.

Student loans often follow borrowers for years, sometimes decades. Even people who fully understand how much they borrowed can feel...

It was a busy week for RIA aggregators. There were a few large moves, including $235 billion multi-family office Cresset...

Blog Posts Archives UnfavoriteFavorite February 27, 2026 Weave: The Social Fabric Project Subscribe to Weave’s Newsletter This story was originally...